Array & ArrayList - Java
개요
- Array 와 cache locality
- Java ArrayList 소스코드 까보기
Array 와 Cache Locality
Array 는 같은 타입을 가진 여러 요소들은 한 곳에 저장하기 위해서 고안되었다. Array 는 할당하는 크기 만큼이 메모리에 연속적으로 할당 되는데 이로 인해 cache locality 을 이용한 빠른 접근이 가능하다.
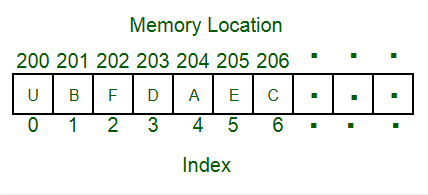
위 사진을 보면 array 내에 있는 각 element 들이 가지는 메모리 주소가 연속적으로 할당되어 있는 것을 볼 수 있다. 캐시 메모리에 대한 간단한 설명을 읽어보면 이해하는데 도움이 된다.
캐시 메모리는 데이터 지역성(Locality)의 원리를 사용한다. 데이터 지역성은 대표적으로 시간 지역성(Temporal locality)과 공간 지역성(Spatial Locality)으로 나뉘는데, 시간 지역성이란 for나 while 같은 반복문에 사용하는 조건 변수처럼 한 번 참조된 데이터는 잠시 후에 또 참조될 가능성이 높다는 것이고, 공간 지역성이란 A[0], A[1]과 같은 데이터 배열에 연속으로 접근할 때 참조된 데이터 근처에 있는 데이터가 잠시 후에 사용될 가능성이 높다는 것이다. - 나무위키
Array 는 연속적인 memory block 으로, array 에 처음 접근할 때 전체 array 가 cache 에 로드된다. 첫 액세스 이후로는 공간 지역성이 생기는 것이다.
Address Contents | Address Contents
aaaa 0000 data[0] | aaaa 1000 l_data
.......
aaaa 0040 data[1] | aaaa 3040 l_data->next
........
aaaa 0080 data[2] | aaaa 4050 1_data->next->next
왼쪽은 array 의 예시이고 오른쪽은 linked list 인 경우의 예시이다. Loop 를 도는 경우에 대해서 각각 생각해 보면, array 의 경우 처음 접근할 때 메모리에서 캐시로 가지고 와야 하지만 한 번 가지고 오면 그 뒤로는 data[1], data[2] 에 는 매우 빠르게 접근할 수 있다. 반면 linked list 의 경우에는 cpu 가 첫 aaaa 1000 주변의 메모리를 같이 cache 한다고 하더라도 다른 데이터들이 연속적인 공간에 있거나 인접한 곳에 있을지 알 수 없기 때문에 매번 메모리에서 다시 가지고 와야 하기 때문에 느리다.
하.지.만. 이것은 C, C++ 처럼 메모리에 직접 접근해서 메모리를 코드단에서 관리해주는 경우의 이야기이고, java 는 jvm 이 알아서 메모리를 관리 하기 때문에 array 사용시 cache locality 가 적용되는지 여부는 jvm 이 메모리 관리하는 방법을 공부해서 좀 더 알아봐야 할 것 같다. 지금 자세한 설명을 할 지식은 없지만 아마 java 에서는 ‘해당사항 없음’ 이라는 결론이 날 것 같다.
Pros and Cons of Array
Array 의 가장 큰 장점은 어떤 요소에 접근하든 random access 에 대한 시간 복잡도가 O(1) 이라는 점이다. 같은 선형 자료구조의 linked list 의 경우 O(n) 이 걸리는 것과 비교해서 read 가 빠르다. 반면 초기에 할당한 size 만큼만 고정으로 사용가능하며, size 를 변경하는 것에 대한 비용이 크다. Size 를 유동적으로 가질 수 있는 array 비슷한 자료형이 java 의 ArrayList 이다.
ArrayList in Java
Java 의 ArrayList 는 AbstractList 를 상속받고 List 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스이다. Array 와 비슷하지만 size 가 dynamic 하게 조절된다.
ArrayList.java 코드를 열어보면 default size 는 10 인 것을 알 수 있다.
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
ArrayList 에서 새로운 element 를 추가하는 메소드는 add() 로, 두 가지 방식의 오버로딩 된 메소드가 정의되어 있다.
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
아래에 있는 add() 메소드는 특정 index 에 element 를 삽입하는 메소드로, 어떤 작업을 한 다음에 기존 array 를 copy 한 더 큰 size 를 가진 새로운 array 를 만들어 낸다. 결국 copy 라는 작업이 필요한 것이다. 그럼 매개변수 하나만 받는 위에있는 add() 는 어떻게 동작하는 걸까?
방금 언급한 어떤 작업 에서 ensureCapacityInternal() 메소드가 사이즈 조절을 담당한다.
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
ensureCapacityInternal() 메소드로 가보면, 사이즈 조절을 위해 ensureExplicitCapacity() 를 또 호출한다. ensureExplicitCapacity() 메소드에서는 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) 이 if 문에 의해 현재 data 를 담고 있는 array 의 length 가 full 이면 grow() 라는 함수를 호출해서 size 를 늘린다.
grow() 함수로 가보면
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); 여기가 포인트다. 비트연산으로 기존 size 의 1/2 만큼 새로운 capacity 를 할당하도록 한다. oldCapacity 값이 10 (default) 이었다면, 10 >> 1 의 경우 10 의 2진수인 1010(2) 을 1-bit right shifting 한 값인 0101(2) , 즉 10진수 5 만큼 size 를 키우는 것이다.
이렇게 size 키워서 결국 한다는 게 copy 다. 결국 java 에서 제공하는 ArrayList 도 별다른 신박한 방법으로 관리하는 array 가 아니라 그냥 array 인 것이다. 즉, size 가 고정되지 않게 하려면 비용이 많이 든다는 단점이 있는 것은 확실하다.
정리
- Array 는 random access 가 O(1) 으로 빠르다.
- Array 는 cache locality 를 이용해 빠른 접근이 가능하나, jvm 에서도 유효한지는 잘 모르겠다.
- Array 는 size 가 고정이고, 처음 할당한 size 와 다른 size 로 조절 하는 비용이 크다.
- 그래서 java 에서는 ArrayList 를 쓸 수 있다.
- 그런데 java 의 ArrayList 도 결국 size 조절에 array 를 copy 하는 방법을 사용하므로 비용이 큰건 같다.