Instrument Rating Checkride Oral Cheat Sheet (Quick IR review)
Intro
- There’s a lot to study for your IR checkride oral, and trying to review everything can be inefficient when you’re short on time.
- So, I’ve summarized and simplified the essential knowledge into a very simple format.
- This isn’t a detailed, in-depth explanation of each topic.
- It’s meant for quick review when you want to rapidly go over everything you’ve studied, especially in the week leading up to your exam.
⚠️ This content is for educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute legal advice or an official FAA guideline. Always refer to the latest FAR/AIM and official regulations for actual flight operations. The author assumes no liability for errors or omissions in the content.
Qualifications
- requirements: AME (age/medical/english) TWEET (training-ground&flight/written/endorsement/experience/training-instrument)
- privilege: PPL privilege + can fly *IR required
- limit: pro rata share
- *IR required: classA / SVFR sunset sunrise / PIC [weather<VFR / pass XC ≥ 50 or night]
- proficiency vs currency: skilled & safe vs min legal req
- unfamiliar: proficiency↓ → workload↑ → risk↑ → mitigate personal minimums & train & POH
- SVFR: clearance to fly in control zone when weather below VFR [ceiling<1000, vis<3]
- aero exp: 50 XC PIC, 40 inst (15hrs CFI, including 250nm filed XC - 3app, airway/routing)
- FTD: BATD max 10hrs, AATD max 20hrs
- PIC: flight review within 24 cal months [1hr-ground/1hr-flight] /w instructor, sub by prac test
- (within 24) 2025.09.16 flight → done at least 2023.09
- carry pass as PIC: 3 TOL 90days, 1 after sunset to 1 before sunrise → full stop
- IFR PIC: 66HITS, SIM (no instructor possible but proficiency↓), airplane (safety pilot)
- last 6 cal months (=exclude current month) → 9/16 IFR flight? 3/1~8/31 log acceptable
- safety pilot: ppl, adequate vision, dual control
- IPC: failed 66HITS + 6 cal month passed → IPC (by CFII, ACS p29, some with SIM)
- today 9/9 → no 6HITS in 3,4,5,6,7,8 → IFR currency expired
- grace period (6 months) → if 6HITS in 9,10,11,12,1,2? then IR current, otherwise IPC required March
- IFR recency exemptions: PIC part 121/135
- logging: soley ref inst, IAF/IF/FAF required (unless radar vectored to final: ATC or safety pilot), simulated IMC (airplane/SIM) → must MDA/DA, actual IMC → FAF pass okay (proficiency↓)
- medical: mine [got my 1st class 2024.06, expires 2029.06.30], 40↓[12/48,12/48,60], 40↑[6/6/12,12/12,24]
- BasicMed: regular physician for medical, bypass AME, alternative 3rd med, require [US driver’s, CMEC 48 months, online course 24 months, treatment, FAA med cert after 7/14/2006], limit [max 7 total, 12500lbs↓, 18000MSL↓, 250kts↓, in US]
Human Factors & ADM
- IMSAFE, PAVE: FAA Personal Minimums Checklist
- hypoxia: oxygen deficiency in body cells, 12000↑, hypoxic(altitude), hypemic(carbon monoxide poisoning/anemia), histotoxic(alcohol/drugs), stagnant(G-force), dizziness/headache
- carbon monoxide poisoning: exhaust fumes, [dizziness/headache], solution [heat-off/vents-open/land ASAPoss]
- hyperventilation: excessive breathing, [dizziness/headache], solution [talk/loud/paperbag]
- body system
- vestibular: inner ear detects [motion/balance] → [pitch/roll/yaw]
- somatosensory: body nerves in [skin/muscles/joints]
- visual (eyes): rods (night & peripheral), cones (color, requires brighter light)
- middle ear & sinus blockage: congestion blocks pressure equalization climb/descend, symptom[ear pain/facial pressure], solution[avoid flying/yawn/chew gums]
- illusions: ICEFLAGS (FA=visual)
- inversion: climb→straight → tumbling backward
- coriolis: head, prolonged turn → trick inner ear → feels tilting/accelerating different direction
- elevator: strong updraft → feels nose-up
- false horizon: visual cues misinterpretation
- leans: slow bank → feels like level flight → actual level flight feels like banking opposite
- autokinesis: stationary light appears to move
- graveyard spiral: prolonged turns → feels like level flight → actual level flight feels like turning
- somatogravic: rapid [acceleration/deceleration] → feels like [nose-up/down]
- oxygen (unpressurized cabin): above 12.5~14 (crew must use after 30min), above 14 (crew entire time), above 15 (each occupants provided)
Regulations & Documents
- personal docs req: PRIM (Pilot cert/Radio license/ID-photo/Medical)
- aircraft docs req: ARROW (A: Airworthiness Certificate)
- maintenance inspections req: AVIATES (A: AD, S: Supplemental Type Certificate)
- preflight: NWKRAFT (Notam/Weather/Known ATC Delay/Runway/Alternate/Fuel/TOL performance)
- max airspeed: 250 [below 10000], 200 [under or VFR corridor class B / 2500↓ within 4NM class C D]
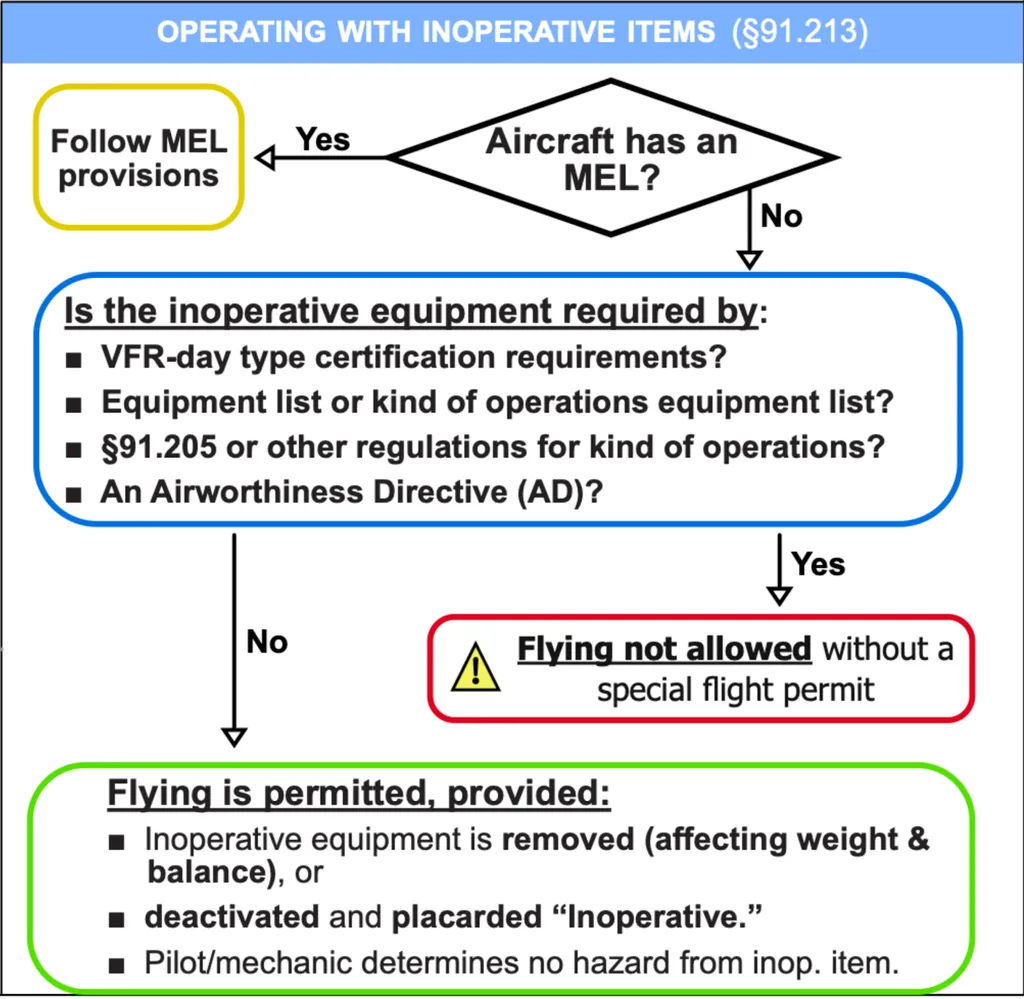
- minimum equip req
- MEL → KOEL → 91.205 → 91.213(d)
- 91.205: ATOMATOFLAMES (VFR day), FLAPS(VFR night), GRABCARD(IFR)
- for hire over water (unless part 121): flotation device for each, at least 1 pyrotechnic signaling device
- above FL240: using VOR → DME/RNAV required
- ATOMATOFLAMES: altimeter/tachometer/oil-pressure/manifold-pressure/airspeed/temperature-engine/oil-temperature/fuel-quantity/landing-gear-position-light/anti-collision/magnetic-direction/ELT/safety-belts
- FLAPS: fuses or circuit-breaker/landing-light/anti-collision/position(navigation)/source of electricity
- GRABCARD: generator or alternator/2way-radio/altimeter(sensitive)/ball(slip-skid)/clock/attitude-ind./rate-of-turn/directional-gyro(heading ind.)
Weather Service & Product
- flight category: LIFR,IFR,MVFR,VFR: vis[1,3,5], ceiling[500,1000,3000]
- sources: aviation weather, 1800wxbrief(web&call), fltplan, EFB(ForeFlight), in-flight [FSS, FIS-B(ADS-B), NEXRAD, ATC]
- ATIS: airport (wind, vis, sky, temp, dew, altimeter, NOTAMs), update hourly (55min)
- AWOS: basic (wind, vis, altimeter, temp, dew, density alt)
- ASOS: more advanced than AWOS+(precipitation type, intensity, runway condition)
- METAR: routine weather report, airport, hourly(55-59min), valid current hour
- SPECI: significant change (vis↓, thunderstorms, wind shifts), update with METAR
- know how to read:
- SPECI KBAF 071007Z AUTO 36003KT 1/4SM R20/2200V3000FT FG VV002 19/18 A2980 RMK A02 T01890183
- KCCA 071015Z AUTO 00000KT 3SM VCTS RA SCT033 BKN080 OVC120 21/21 A2986 RMK A02 LTG DSNT ALQDS
- KBOS 251911Z 32006KT 5SM TS SCT055 BKN070CB OVC090 26/22 A2982 RMK A02 PK WND 26027/1855 RAE10 OCNL LTGICCC E TS E MOV E P0010 T02610217 $
- PIREP: real-time by pilots, UA(routine), UUA(urgent, turbulence, icing)
- UA /OV LAX090015 /TM 1500 /FL050 /TP C172 /SK SCT025-TOP030 /WX FV04SM /TA 10 /TB LGT /IC NEG
- UUA /OV MYR180001/TM 1422/ FLDURD/TP CRJ7/WV +15 AT 400 FEET -20 AT 200 FEET
- TAF: by meteorologists, forecast, 5SM radius around station, every 6hours (4 times a day - 00, 06, 12, 18), 24/30 hrs
- TAF AMD (amended, supersede previous TAF), TAF COR (corrected)
- TEMPO(temporary, lasting less than 1hr), FM (rapid change within 1hr), BECMG (gradual change up to 2hrs), PROB (probability, PROB30 → 30% chance)
- know how to read:
- BECMG 3000/3001 VRB05KT 9999 NSW FEW050 SCT090 QNH2987INS TX23/2920Z TN11/3010Z
- 042025Z 0420/0523 1901520KT 9999 SCT060 BKN250 QNH2975INS WND 17009KT AFT 0502 TEMPO 0420/0501 21015G25KT 520005
- winds aloft (FB): various altitudes, 4 times daily, (no wind 1500↓AGL, no temp 2500↓AGL), for [choosing alt/fuel plan/icing/freezing level/lapse rate/temperature inversion/turbulence], “7525-02”
- AIRMET (WA): non-scheduled inflight advisory, hazardous light aircraft, valid 6hrs, S(mountain obscuration), T(srf wind≥30, turbulence, low-level wind shear), Z(icing, freezing level)
- SIGMET (WS): non-convective severe, for all aircraft, not associated with thunderstorms, valid 4hrs (6 if hurricane), severe turbulence (CAT), severe icing, volcanic ash, dust/sand storms reducing vis to ≤ 3S
- Convective SIGMET (WST):
- severe convective weather, hazardous to all aircraft, hourly at H+55, valid for 2hrs (severe or greater turbulence, severe icing, low-level wind shear)
- convective?: vertical movement of air caused by heating → thunderstorms & lightning
- issued for: (not for Alaska/Hawaii)
- thunder-storm: areas ≥ 40% of 3000sq miles
- severe thunder-storm: surface wind≥50kts, hail at surface ≥ 3/4 inch in diameter
- embedded thunder-storm: obscured by cloud layers
- squall line thunder-storm: at least [60 miles long & affecting at 40% of its length]
- Convective Outlook (AC): forecasting tool, broad view of t-storm. expectation, available SPC, 8 day outlook (1,2,3,4-8), issuance [day1(5times), day2(2times), day3(1time)]
- NEXRAD: ground-based radars, not real-time (5-20min delay), detects [t-storms, precipitation (heavy rain), wind speed, atmospheric motion]
- surface analysis chart: snapshot of current weather, on the ground, every 3hrs, provides[H/L, fronts, isobars, weather symbols (rain/fog)]
- prognostic chart: forecast of future weather, 6/12/24/48 hrs ahead, 4 times daily, provides[H/L, fronts, isobars, weather hazards (turb/icing/precipitation)]
- CVA: ceiling & visiblity analysis, graphical weather, quick overview of ceiling & vis
Weather Theory
- abbreviation for this section: t-storm(thunderstorm), vis(visibility), w.(wind), p.(pressure), turb(turbulence), cl.(cloud), ws(wind shear), alt(altitude)
- atmosphere: [nitrogen78/oxygen21/argon0.9/water-vapor0-4]%
- standard day: 15℃ (59℉), 29.92”Hg (1013.2hPa or mb)
- heat exchange: sun uneven heating → warm(less dense)↑ & cold(denser)↓ → air movement
- stable air: resists vertical motion, stratiform, smooth air, steady precipitation, fair-poor vis
- unstable air: promotes vertical motion, towering(cumuliform), rough air, showery precipitation, t-storms., good vis
- lapse rate: rate at which temp↓ as alt↑, standard 1000’↑ [2℃/1”Hg]↓, steeper(temp↓rapidly as alt↑) → unstable/convective act
- temp inversion: temp↑ as alt↑, hot-day&cool-night→ ground cools → still hot above → warm air lid → trapping cooler air → vis↓(smog/haze),wind shear
- wind shear: sudden change wind speed/direction in small area
- sudden drastic change in IAS, affect lift & control, low-level ws (less time to recover)
- mainly occurs: t-storms, frontal boundary (cold front), temperature inversion, CAT at high, microbursts
- mountain wave: strong w. blow perpendicular to mountain, severe turb, lenticular/rotor cl.
- factors affecting wind:
- pressure diff [diff↑→wind↑]
- coriolis force: earth’s rotation, deflect wind/air right Northern Hem., poles↑equator:0
- friction btwn air/surface: slows down wind→coriolis force↓→wind flow across isobars at slight angle toward low pressure (surface wind slower & turb. than winds aloft)
- gravity: vertical air movements (downbursts/microbursts)
- isobar: connect points equal pressure, closer→pressure gradient↑→wind↑
- high pressure: air moves[outward/downward/clockwise], typically clear&stable, sinking air warms up→preventing clouds forming
- low pressure: air moves[inward/upward/counter-clockwise], generally cloudy&unstable, often rain/snow, rising air cools→moisture condense→[form clouds,icing risk]
- trough: brown, elongated area of low p., air↑(can’t sink or spread)→cloud forms&precipitation→often bad weather
- ridge: yellow, elongated area of high p., air↓→often good weather
- turbulence: unsteady/irregular motion of air
- thermal turb: hot days→uneven heating→warm air↑→cumulus clouds & storms
- mechanical turb: wind blowing over [rough ground/mountains]→choppy air
- frontal turb: two air masses(cold front)→warm air↑→instability&bumps
- CAT: invisible in clear sky, often near jet stream (due to strong wind shear)
- dew point: temperature at which air becomes saturated → no longer hold water vapor → condensation begins (water vapor → liquid)
- closer temp&dewpoint→humidity↑visible moisture↑(fog/clouds/dew/frost/rain)→ vis↓
- aircraft surface == dew point → frost
- temperature < dew point → icing
- precipitation: any form of water that falls from the atmosphere (rain/drizzle/sleet/hail)
- sleet: snow(solid, ice crystals)+freezing rain(rapid structural icing)
- hail: ice pellets produced by strong updrafts in thunderstorms
- fronts: boundaries between two air masses
- squall line? → ahead of a cold front
- cold front moves over mountainous? → icing
- frontal waves? → slowly moving cold fronts or stationary fronts
- low level wind shear? → warm front (temperature inversion)
- cold front (blue): [cold/dense/fast-moving/20-30kts or faster] air forces warm air to rise rapidly → steep frontal surface, generally more intense (after:temperature↓&clr sky)
- hazards: rapid weather change(few hours), towering cumulous(nimbus), strong turbulence, gusty winds, heavy precip, squall line t-storms., hail, tornadoes
- warm front (red): [warm/less dense/slow-moving/10-15kts] air glides up over cooler air mass → gradual frontal slope, generally less intense, produce [wide area of weather/stratiform/ceiling↓/vis↓/rain/drizzle&fog]
- hazards: freezing rain → icing (warm rain falls into cold air layer and freeze)
- stationary front (red&blue): two air masses balanced, neither is advancing, can last for days, mixed cold&warm fronts, hazards[low-intensity precip, poor vis, low cloud]
- occluded front (purple): fast-moving cold front catches up slower-moving warm front → lifting warm air mass entirely off the ground, mixed cold&warm fronts
- hazards: strong winds/turbulence/embedded thunderstorms with thick cloud layers]
- more severe when warm front occlusion (embedded thunderstorms)
- clouds: moist air cooled to its dew point → water vapor condenses into tiny liquid
- caused by lifting: convective(air heated&rise), orographic(air rise by mountain), frontal
- hazards: icing, turb(cumuliform clouds), vis↓, thunderstorms
- cloud types: cumulus(piled), stratus(in layers), cirrus(high-level,20000↑), nimbus (rain-bearing), alto(middle-level,5000-20000)
- lenticularus: lens-shaped, formed over mountains in strong winds
- virga - contains strong downdrafts
- rotor clouds
- thunderstorm: unstable(steep)lapse rate, sufficient moisture(small temp-dewpoint spread), lifting action(surface heat, orographic, frontal)
- thunderstorm stages: cumulus[cloud develop/strong updrafts], mature[most intense/up&down-drafts/rainfall begins/severe turb/wind shear/lighting/hail], dissipating[weakens/mostly downdrafts/rainfall decrease/often anvil top]
- thunderstorm caution: keep 20NM distance (hail/rain can be thrown up to 20NM)
- microburst: [undetectable/small/strong]downdraft→sudden/powerful winds near ground
- losing altitude 6000ft/min, dangerous WS(especially takeoff/landing)
- wind(150mph=131kts), short-lived, lasting 5-15 min, less than 2.5 miles wide
- fog (PAIRUS): cloud near surface(50’), air cools to its dew point & moisture added
- precipitation: rain→moisture evaporates→humidity↑→air saturated, warm rain through cooler air[warm front/temperature inversion]
- advection: warm/moist air moves over cooler surface (coastal areas), opposite of steam fog, forms quickly, cover large areas
- ice: extremely cold (below -25°F), Arctic regions
- radiation: calm/clear night, ground cools air above, dissipate with sunrise
- upslope: wind pushes moist/stable air to upsloping terrain (mountain obscuration)
- steam: cold/dry air moves over warm water
- fog vs mist: fog(vis<5/8mile), mist(5/8≤vis<7) is often dissipating form of fog
- frost: surface below freezing, water vapor condenses onto that surface
- effects: even thin layer→significantly disrupt airflow→lift↓drag↑→stall speed↑
- hazards: dangerous especially during takeoff, block [pitot tubes, static port]
- removal: [anti-icing/de-icing] fluid, wipe off, melt in [heated hanger, sun]
- freezing rain: rain→ice (it was rain above but freezes at current altitude -> rain that starts to freeze)
- temperature inversion: above warm layer → cold → snow → [snow→rain] at warm layer → [rain→ice] at cold surface → ice pellets at surface means [freezing rain/supercooled water] at higher altitude
- rain from air 0℃↑ → into air 0℃↓
- rain freezes on impact
- temp could be 0℃↑ at higher alt.
- freezing drizzle→warmer air above
- wet snow: ice→rain (it was snow above but melts at current altitude -> snow that starts to melt)
- wet snow at your alt.→ temp>freezing → freezing level above
Icing
- PA28: defroster, carb heat, pitot heat
- intensity: trace, light, moderate(accumulation 1~3inches/hour), severe
- low-pressure areas: rising air → cool down → visible moisture↑ → icing risk↑
- performance degradation:
- 1/2 inch ice → lift↓ by 50%
- icing→disrupts airflow(lift↓thrust↓drag↑weight↑)→AoA↑→stall speed↑
- approach speed↑, landing distance↑
- sandpaper-like icing on leading edge and upper surface → lift↓by30%&drag↑by40%
- mitigate: icing&rolling→use aileron↓rudder↑, tailplane stall→use caution app&land, disengage auto-pilot VS mode, deicing, anti-icing
- hand fly, find cloud base/top, leave visible moisture (climb/descend/turn), warmer temperature, lower humidity
- in some cases, reaching -10℃ could be an option, since visible moisture is less likely to be present
- types: instrument, induction, structural
- instrument icing: forms on instruments & sensors → inaccurate readings → pitot-heat
- induction icing: forms in engine’s air intake system → airflow↓ → disrupts air/fuel mixture → engine performance↓ → engine failure (carb icing)
- carburetor icing: forms when [temperatures (-7~21℃, 70℉) / relative humidity above 80%], due to steep temperature drop in carburetor venturi → carb heat
- structural icing: forms when visible moisture contacts below freezing aircraft surface, forms on exterior surface (wings/tail/props) → change airfoil shape → risk↑
- clear: large droplet spreads. [smooth/clear/hard/dense]→difficult [detect/remove]
- rime: small droplets freeze instantly. [milky(rough&white) color, brittle texture] → easier to spot, forms on thinner parts (wing edges)
- mixed: when [snow/rain] coexists(unstable/mixed clouds), severe performance loss
- +structural icing: “most likely”→freezing rain (“least” likely→high clouds), mostly form on tail in rain when temperature few degree above freezing, opposite of ICTS
- SLD (Supercooled Large droplets)
- liquid water droplets that remain in a liquid state even at temp below freezing.
- occur aloft even without precipitation at surface.
- visual indication: droplets that splash on impact at temperatures below 5℃
- freezing level: lowest altitude temperature 0°C, must get accurate freezing level before IFR, sources [AWC/winds aloft forecast (FB)/PIREP/weather briefing]
- FIKI: [frost/ice/snow] on airplane→not allowed, but deicing or anti-icing equip to protect[wings/windshield/controls/instrument]? → allowed (use caution)
- icing on airfoils: shape change→weight↑lift↓(less noticeable at low AoA)→stall speed↑
- small ice→localized stall→roll/spin, likely form first on tailplane, flaps already extended?(never retract)→retract?→stall speed↑
- roll upset: can be caused by localized stall, try [AoA↓/airspeed↑/extend flaps/wings level]
- tailplane: tailplane creates tail-down force→nose-up moment→counteracts nose-down moment created by lift, better ice collector than wings
- tailplane icing (ICTS): Ice Contaminated Tailplane Stall, mostly during approach/landing
- tailplane icing→tail-down force↓→nose-down↑ ← don’t [deploy flaps or speed↑]
- if flaps or speed↑→lift↑→even more nose-down
- symptoms: elevator[vibration↑effectiveness↓heavier] & uncommanded nose-down
- recovery: retract flaps immediately, and then speed↑ to counteract flap retraction, slowly control nose-down pitch, no-flaps approach
- tailplane icing→tail-down force↓→nose-down↑ ← don’t [deploy flaps or speed↑]
- plan&predict (CAFFU): Cloud layers, Air temperature & pressure (more likely in low-pressure areas, cool temperatures), Fronts movement, Freezing level, Use weather briefing (METAR/TAF/AIRMET/SIGMET)
- anti-icing/deicing: anti-icing(prevention), deicing(removal)
- for airfoil: inflatable deicing boots, thermal anti-ice leading edge, weeping wings
- for windshield: alcohol anti-ice, electric heating anti-ice, defroster
- for propeller: alcohol anti-ice, electric heating anti-ice, deicing boots
- others: pitot heat, carb heat
Instrument & Attitude Flying
- basic skills: CIA, errors: fixation/omission/emphasis
- set power & attitude, then monitor performance
- (first) control: power [tach/manifold p.], attitude (attitude ind.)
- (second) performance: pitch [altimeter/ASI/VSI], bank (heading ind/turn cord./mag.comp]
- primary & supporting
- pitch: attitude ind., altimeter, airspeed, VSI
- bank: attitude ind., heading ind., mag. compass, turn cord.
- power: airspeed, tachometer, manifold pressure
- primary instruments: not moving / not changing
-
table
Maneuve r Pitch Bank Powe r Straight & Level Altimeter Heading Airspeed Climbs / Descents (Airspeed) Airspeed Heading VSI Climbs / Descents (Vertical Speed) VSI Heading Airspeed Turns Altimeter Turn Coordinator Airspeed Transition to Climb Attitude Heading VSI/Airspeed Transition to Turn Altimeter Attitude Airspeed ILS Approach Glide Slope Localizer Airspeed
- pitch: attitude ind., altimeter, airspeed, VSI
- gyroscopic principles
- rigidity in space: spinning gyro remains fixed in its plane of rotation, providing stability
- precession: force is applied to gyro, resulting force occurs 90° ahead in the direction of rotation
- gyroscopic instruments
- att ind: bank/pitch, rigidity in space, vacuum-driven or elec, correct in 5 start engine, errors[acceleration?/deceleration?/roll-out?]
- head ind: heading, rigidity in space, vacuum (calibrate w mag.com) or elec
- turn ind: rate-of-turn & rate-of-roll, precession, turn coordinator (both), turn-and-slip ind (rate-of-turn only)
- pitot-static instruments: pitot tube (dynamic p), static port (ambient static p), pitot mast
- altimeter: measure altitude above specific ref (sea level, Kollsman window), 75ft airport elev, High to Low Look out Below
- how: altitude↑→pressure↓→wafer expands→mechanical linkage→indicate
- VSI: shows rate-of-climb in fpm, 6-9sec delay, rate trend immediate
- how: diaphragm direct static source, chamber receives static p via calibrated leak, climb/descend→diaphragm p change instantly, chamber change slowly→pressure diff→mechanical linkage→shows rate of climb
- ASI: measures diff between impact(ram) air p (pitot tube) and ambient p (static port)
- how: dynamic p (airspeed)=impact p - static p, diaphragm receives ram air p from pitot tube [faster→expand], air p↓ as alt↑ → ASI indicate slower → to correct → apply ambient p from static port → shows dynamic p as airspeed
- altimeter: measure altitude above specific ref (sea level, Kollsman window), 75ft airport elev, High to Low Look out Below
- types of altitude: indicated, true (actual/MSL), absolute (AGL), pressure, density
- PA: corrected for non-standard p. (FL180↑→29.92), formula
- DA: PA corrected for non-standard temp, formula
- [pressure↓/humidity↑/temperature↑] → DA↑ → less dense air → performance↓
- DA ↑ → [takeoff & landing roll ↑ / rate of climb ↓ / same IAS but TAS ↑ on landing]
- types of speed: IAS, CAS (IAS corrected for instrument & position errors), TAS (CAS corrected for pressure & non-standard temperature), GS (TAS corrected for wind)
- markings: white-flaps (Vso~Vfe), green-normal (Vs1~Vno), yellow-caution, red-Vne
- Vspeeds(PA28): Vs0(44),Vs1(51),Vne(160),Vno(126),Va(88-111),Vfe(103),Vy(79),Vx(63),Vg(73,LDmax),Vb(87,Vs1*1.7),landingfinal(63),crosswind(17)
- pitot-static blockage
- static port: airspeed (alt↑→speed↓, correct only at blocked), altimeter(freeze), VSI(0)
- using alternate static source → venturi effect → lower pressure
- airspeed↑, altimeter↑, VSI (momentarily climb)
- pitot tube: use pitot-heat
- ram air inlet (x) & drain hole (o) → 0 (zero)
- ram air inlet (x) & drain hole (x) → like altimeter
- instrument taxi check: ASI 0, VSI 0, altimeter ±75ft, heading correct, att (bank ±°5 within 5 minutes of engine start, if vacuum), turn cord (turn → ball goes to opposite), compass (swings freely, full of fluid)
- magnetic compass err VODM: variation(diff true N mag N, east least west best), oscillation(swinging needle turb or maneuv), deviation(aircraft mag field), magnetic dip (earth’s magnetic field pulling needle down, north affinity, acc decel error ANDS, turning err UNOS)
- electronic flight inst: AHRS, ADC, FD, FMS, EFIS
IFR rules
- IFR flight plan: FSS[radio/phone/RCO/person], ARTCC, online[1800/fltplan/EFB], 30min prior dep (4hrs before if FL230↑), cancel[towered:auto, non-to:pilot→ATC/FSS, anytime out A or no IMC], form [7233-4 INT, 7233-1 FAA]
- your filed plan will be shown on ATC’s side for 2 hours
- min fuel: dest, alt, 45min cruise
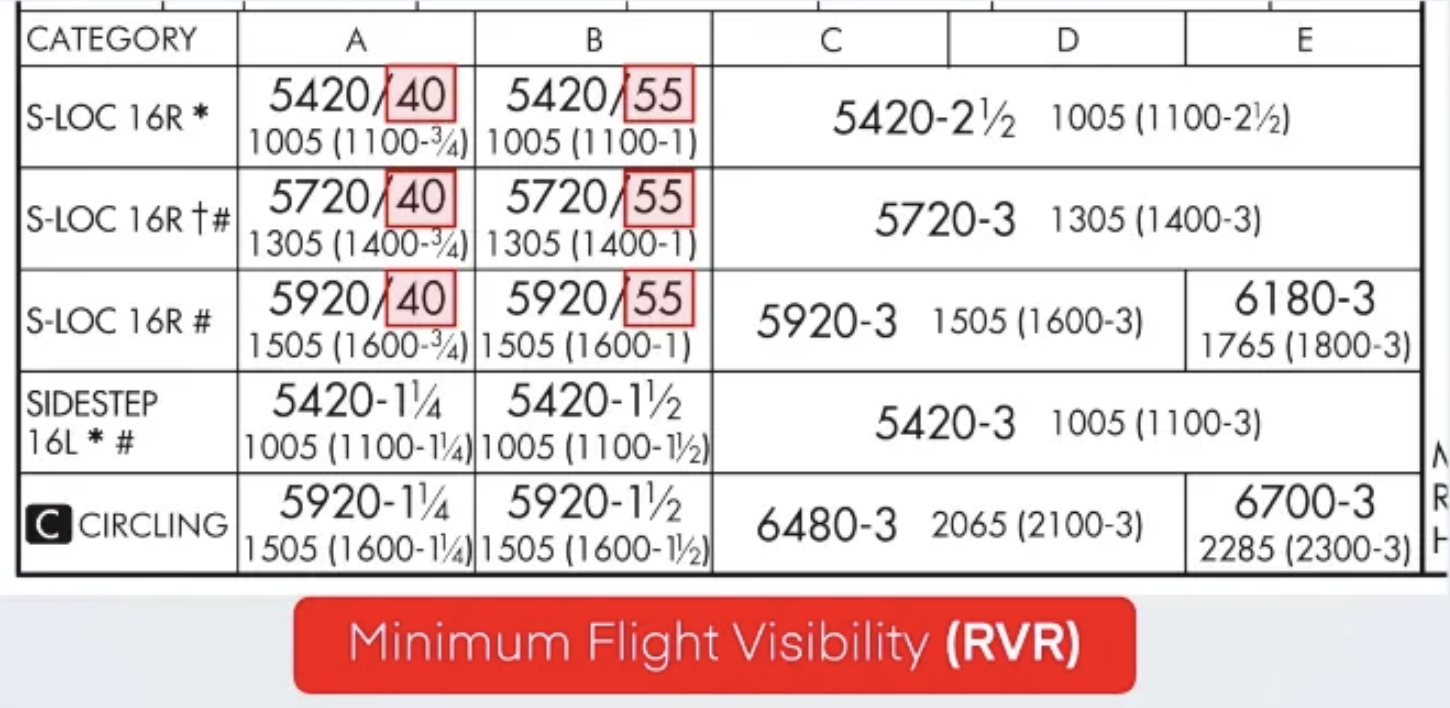
- alternate required: 1123 (11ETA, ceiling 2000, vis 3SM)
- alternate airport weather minima: 600/2 precision, 800/2 non-precision, no IAP?→ceiling & vis desc MEA, app & landing VFR
- GPS considerations: non-WAAS (1 GPS app), no baro-VNAV WAAS (plan LNAV both), baro-VNAV WAAS (plan LNAV/VNAV or RNP0.3 both)
- IFR cruising alt: →odd, ←even, MC, above FL290, RVSM
- IFR takeoff minimums: part91[priv/GA/train] none, part121/135 (1-2eng:1SM, eng>2:1/2SM), even though 91[vis↓&ceiling↓→ODP→if 200f/nm not avail→VCOA]
- IFR min alt: not allowed ↓min-altiutde, if none → mountain 2000/4, non-mountain 1000/4
- required reports: MARVELOUS VFR C500 == fix/points: MCFOH, change: AEA, safety: US EU (CFO, E: non-radar)
- position reports: IF TPA fix/point/remarks [ID, flight plan type, time, position, altitude, next reporting fix (ETA & name), next succeeding point (name), remarks]
- other keywords: cruise clearance, block altitudes, minimum fuel (non emergency)
IFR Flying Procedures
- DP: TO→ENR transition, [DER35’/400’turn/200FPNM], course guidance [10NM straight, 5NM turn], ODP/SID(workload↓, graphic), not required but encouraged [night/MVMC/IMC]
- Diverse DP: IAP but no DP, requires airport no obs 200FPNM up to min IFR alt, turn 400’, DVA
- VCOA: designed to avoid 3SM from DER, visual climbing turn up to published alt, alternative for >200fpnm, advise ATC
- clearance: after 30min CVT ATC, EDCT 5min, how (clearance/ground/pop-up/PDC/CPDLC), hold for release (traffic mgmt, class D only 1 IFR, hold until “released for departure”), “expect 3000 10 min after”→clearance limit for lost comm
- VFR-on-top: by pilot request, only FL180↓(no class A), at above MEA, comply IFR regulations, VFR cruising alt, VFR cloud clr & vis req, report reaching VFR-on-top
- STAR: ENR→APPR transition, [flow/sequencing] for busy, at least a textual required, “No STARs” remarks, RNAV STARs RNAV1 performance
- holding: for [missed/delay/traffic/weather/emergency], clearance items?, reduce speed 3min before, 5T, min of [3°sec/30°bank/25°FDS], speed limit [~6~14/200,230,265], inbound [14000↓1min, 14000↑1.5min], leave [EFC/ETA if lost comm/report]
- lost comm: 7600, “in the blind”, Highest MEA (minimum IFR alt., expected, assigned), route orderly AVEF (Assigned, Vectored, Expected, Filed), VFR ASAPrac, light-gun
- leaving clearance limit
- if c-limit is approach begin fix: start descend & approach as close as possible to EFC (if no EFC → ETA)
- if c-limit not approach begin fix: leave c-limit at EFC
- if no EFC: upon arrival over the c-limit, proceed to a fix where approach begins and commence descent as close to ETA
- PT: course reversal, descent from IAF, 10NM, max 200kts, NoPT, SHARPTT
- NoPT when SHARPTT: straight-in/holding-in-lieu-of/DME Arc/radar vectors/NoPT/time approach/teardrop course reversal
Navigation
- VOR
- full deflection 10° (5 dots, 2° deviation for dot), verify morse ID
- check: [VOT±4/ground±4/airborne±6/dual-check 4 between two], every 30 days, check FROM 0 / TO 180, sensitivity (at 5th dot within 10°~12°)
- sign: DEPS (Date / bearing Error / Place / Signature)
- limit: cone of confusion (1 mile per 10,000ft), reverse sensing, require line-of-sight
- DME: auto tune with (VOR/LOC), slant range error (right above 6076ft shows 1NM), negligible 1NM per every 1000ft (you 5000ft? → negligible when 5NM away)
- NDB: low-mid freq band, older form → replacing, how: [sends signal all direction → ADF (automatic direction finder) points needle to NDB station]
- ILS: instrument landing system, localizer, glide slope, marker beacons,
- ILS failure: outside FAF (→switch LOC), inside FAF(→Missed)
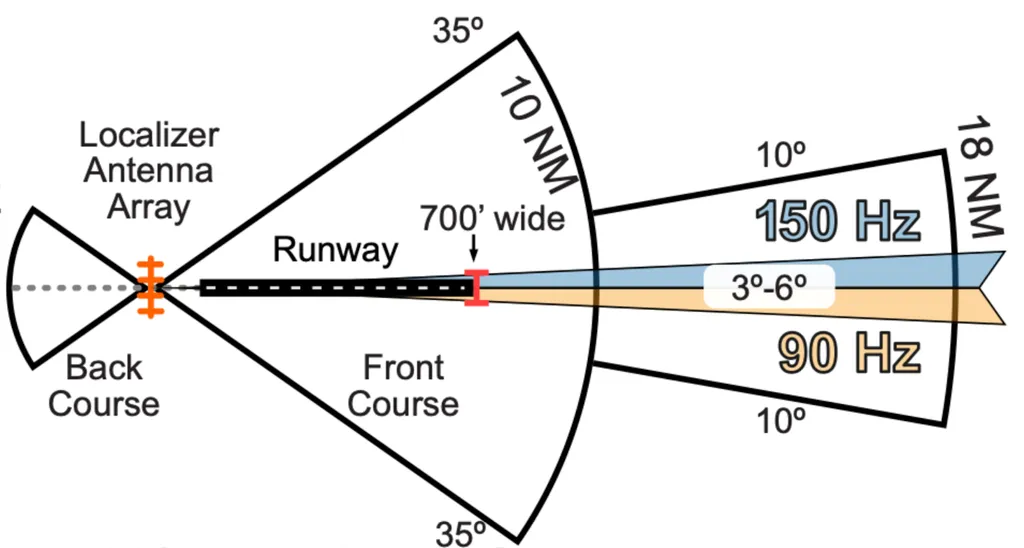
- Localizer: opposite end of rwy, lateral guide, width (3°-6°), threshold 700ft (350ft each from center), usually 5° total width (2.5° each side → 4x sensitive than VOR), coverage[10NM-35°/18NM-10°/4500ft]
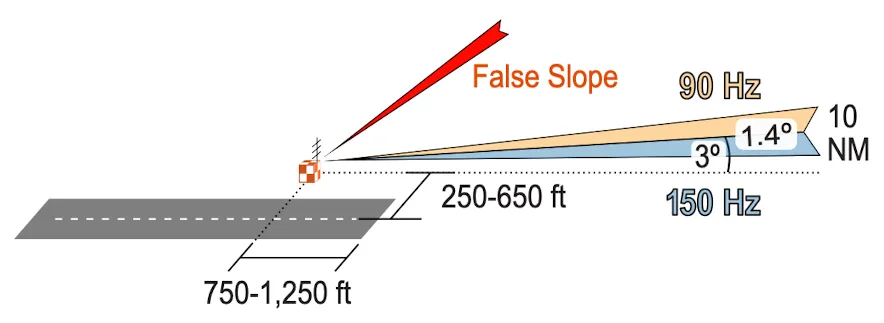
- glide slope: vertical guide, auto tune /w LOC, interprets 90Hz/150Hz signal (90Hz>150Hz → above), width (1.4°, 0.7 for up/down deach), range (10NM), slope (3°)
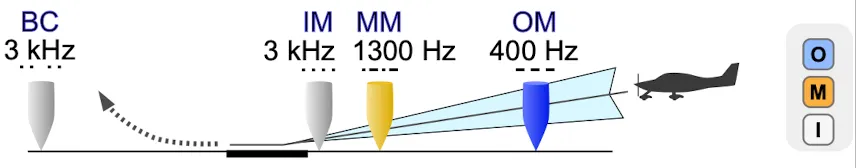
- marker beacons: provides range information
-
Marker Beacon Color Audio Pattern Distance from RWY Height (AGL) Outer Marker (OM) Blue — (slow) 4~7miles (21000~37000ft) about 1400ft Middle Marker (MM) Amber -.-. (middle) 0.5~0.8miles (2600~4200ft) about 200~250ft Inner Marker (IM) White ….(fast) near threshold (within 300~500ft) below 100ft
-
- GPS keywords
- update every 28 days
- GNSS: all satellite system world-wide, including GPS (US GNSS - dep of Defense)
- GPS: type of GNSS, operate by US dep of Defense
- SBAS: ground stations → accuracy 10x↑, [WAAS(US)/EGNOS(EU)/KASS(KOR)]
- WAAS: type of SBAS, FAA run, [error margin 3 meters / position accuracy 95%↑]
- GBAS: installed near airport, GLS can replace ILS, accuracy↑ than WAAS but coverage↓)
- RAIM: detects satellite error → gives warning, min 5 functioning required, WAAS GPS no need RAIM but built for backup
- TSO-C[129,196]: non-WAAS GPS, no SBAS correction, alternate require non-GPS
- PBN (set of standard), RNP (type or RNAV, RNAV with alert, RAIM, WAAS)
- RNP0.3 (APPR), RNAV1 (DP, STAR), RNAV2 (ENR)
- approved GPS: G1000, GNS 430/530, GTN750 (↔ non approved:ForeFlight)
- RNAV (Area Navigation): fly any path using its own equip, without overfly ground-based facilities, types[GNSS,VOR/DME,DME/DME], no GPS RNAV possible
- RNAV NavSpecs: lateral navigation accuracy, RNAV1 [DPs/STARs]: less 1NM err 95%, RNAV2 (enroute,T/Q-routes): less 2NM err 95%, RNAV10 (for oceanic)
- how GPS works
- 5 satellites at any location→each satellites sends time-stamped signal→receiver measures travel time of signal→calculate distance to each satellite
- 3 satellites → position (lat/long), 4 satellites → position & altitude
- RAIM: GPS receiver monitors satellite signal integrity, min 5 (or 4+ altimeter input (baro-aided RAIM)), fault exclusion → min 6 (or 5 + alt input)
- PBN: set of navigation equip standards (particular NavSpecs), not dependent on single tech, procedure don’t need to be changed/renamed just because of new nav hardware
- RNP: type of PBN, “statement” of nav equip and service performance
- RNAV: no alerting
- RNP: type of RNAV + [monitoring/alerting] function (RAIM or WAAS)
- RNP0.3 approach: nav. sys. must maintain accuracy of 0.3NM or better from runway centerline during final approach segment → accuracy<standard?→alert
- RNP approach minima and equipment:
- GLS DA minima → require GBAS
- LP MDA / LPV DA minima → require RNP achieved by WAAS.
- LNAV / VNAV DA → achieved by VNAV-approved WAAS, or BARO-VNAV systems.
- LNAV MDA → achieved by a basic, unaugmented IFR-approved GPS.
- RNP Navigation Performance
- Final Approach: RNP 0.3 (0.3 NM accuracy 95% of flight time)
- Terminal & Departure: RNP 1.0 (1 NM accuracy 95% of the flight time)
- Enroute: RNP 2.0 (2 NM accuracy 95% of the flight time)
Approach
- stabilized approach: landing config, on profile, airspeed±10, descent rate 500~700 (no more than 1000), optimal RPM
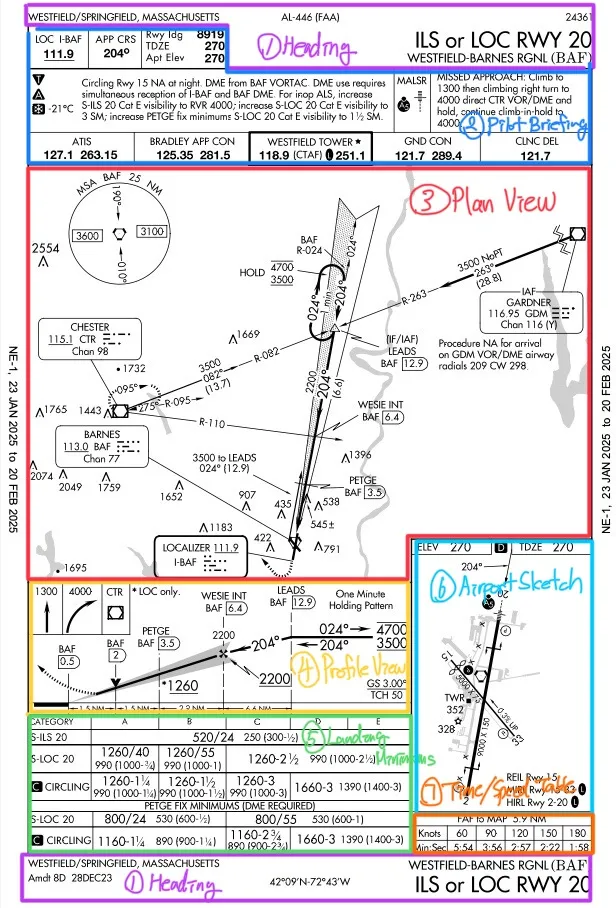
- chart reading: TDZE(highest in first 3000’), THRE(threshold elev.), MSA(guarantees 1000’ obs. clear. within 25NM radius, no sig coverage), TCH (threshold crossing height)
- signs[T/A/Ana]: T[non-standard TO mins / DP], A[non-standard IFR alternate min], Ana[alternate minimums not authorized=can’t be used as alternate airport]
- signs[snowflake]: Cold Temperature Airport X mark → altitude correction (AGL), AIM 7-3 correction table (how far below due to cold temperature induced error)
- identify FAF: precision (light-bolt), non-precision (maltese cross)
- approach category
- Based on final approach speed (1.3 times stall speed in landing configuration at MGLW (maximum gross landing weight))
- A ≤ 90, B (91-120), C (121-140), D (141-165), E > 165
- descend below MDA/DA (91.175): normal descent rate, not less than visibility requirement, visual reference requirement
- visual reference requirements: runway environment in-sight
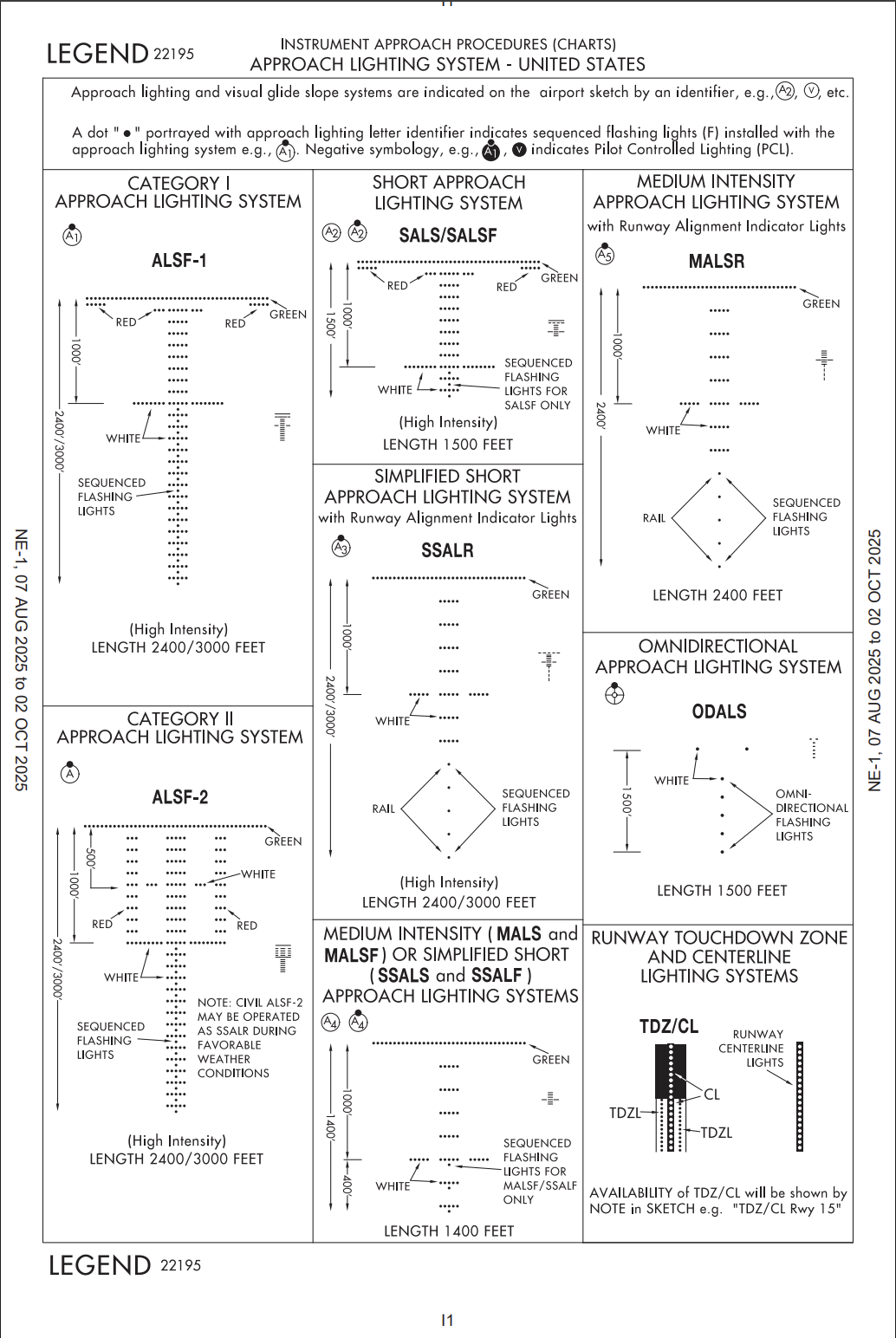
- [threshold, runway, touchdown zone] markings or lights, REIL, VASI, PAPI
- ALS : red terminating bars (ASLF-1) or red side row bars (ALSF-2) → descend below 100ft above TDZE
- missed approach
- identify [precision: DA / non-precision: MAP]
- execute when: “MDA→MAP or DH/DA” with insufficient visual ref, unsafe app, ATC
- immediately go-missed when: CDI deflects 3/4-scale↑ (horizontal/vertical), RAIM lost, when below MDA/DA (visual contact lost, vis<minimum, not in normal pos.)
- approach clearances: when can you descend to next approach segment? → cleared for app. & established on segment of published app.
- VDP: non-precision, ‘V’ symbol on profile, no below MDA prior to reaching VDP
- no VDP? → maintain MDA until 91.175 is met → descend
- VDP on chart? then maintain MDA to VDP (even if 91.175 is met)
- at VDP? → 91.175 meet? then descend, otherwise go missed
- formula: (MDA in AGL) / 300 → NM, (MDA in AGL) / 10 → sec
- VDA: glide path from FAF to TCH (for non-precision), typically 3°, advisory only
- IAP (Instrument Approach Procedures)
- precision: ILS, MLS, PAR, GLS, TLS → lateral & vertical guidance to DA
- non-precision: VOR, LOC, RNAV/RNP to LNAV or LP Minima, LDA, SDF, ASR, NDB → lateral only to MDA, step-down
- NDB, VOR, LOC: may use IFR-certified GPS as primary source until the FAF
- APV: prevision-like, to DA, with vertical guidance but doesn’t meet precision standard
- LDA with Glide Slope, LPV, LNAV/VNAV
- other types of approach: circling/visual/contact/radar-vectors/parallel/GLS
- circling: course alignment↔rwy center exceeds 30°, approach name not include rwy (VOR/DME-B), remain 1.3NM (for category A) radius of all runways (B1.5, C1.7, D2.3, E4.5), visual ref lost while circling? (climbing turn to landing rwy → continue turn until established on missed course)
- visual: pilot or ATC initiate (pilot can reject), vis≥3SM, ceiling≥1000 (IFR under VMC), must have [airport or traffic to follow] in-sight, pilot responsible visual separation
- contact: similar to visual but SVFR, only init by pilot (no ATC), airport with IAP (ground vis≥1sm, remain Coc), obs. clr. pilot’s responsibility
- radar vectors to final: at least 2NM outside FAF, until cleared [no turn to final / maintain last assigned altitude]
- parallel ILS: provides 1 1/2 miles radar separation between aircraft
- GLS: only 3 airports, KEWR, KIAH, Boeing private
- LPV vs LNAV/VNAV:
- LPV: requires WAAS, GPS based, no temperature error
- LNAV/VNAV: non-WAAS ok, GPS + baro-VNAV based → temperature error
Airspace & IFR Low Chart
- special user airspace: MCPRAWN
- MOA: military training zones, permission NOT required, but extreme caution (advised to contact the controlling agency)
- Controlled firing: NOT ON CHART (means no one knows where the controlled firing space is), potential hazards (firing will be stopped if an aircraft is detected)
- Prohibited: [P-**], security reasons, NOT ALLOWED
- Restricted: [R-**], hazardous activities, PERMISSION REQUIRED if active
- Alerting: [A-**], high traffic volumes (ex. pilot training). exercise caution.
- Warning: [W-**], potential hazards, 3NM off the U.S. coast.
- NSA (national security area): temporarily prohibited, not to enter voluntarily, ADIZ (2-way radio, transponder, file IF or DVFR)
- (+) TFR: prohibited without authorization. check NOTAM.
- (+) SFRA (Special Flight Rules Area): Grand Canyon, Washington DC, Hudson River
- minimum altitude for IFR
- no applicable minimum altitude? → mountainous (2000↑ highest obs., 4NM horizontal), others (1000↑ highest obs., 4NM horizontal)
- DA(DH): precision, above rwy threshold
- MDA(MDH): non-precision, above wy threshold, visual references
- MCA: route & direction, must cross higher than MCA, flying to higher MEA, X flag
- MTA: obstacle clearance (vertical/lateral) turns over fixes
- MRA: lowest alt for nav signal. R flag
- MEA: nav signal reception & obstacle clearance (along airway), MEA GAP
- МОСА: obstacle clearance (could be lower than MEA), guarantees VOR signal within 22NM(25SM) of station, * sign
- MVA: could be lower than MOCA, assigned by ATC.
- OROCA: obstacle clearance within 1° grid square, no signal guaranteed (VFR MEF)
- MAA: max authorized alt
- MSA: guarantees 1000ft obstacle clearance within 25NM, no sig coverage
- airport: blue/green (IAP), brown (no-IAP), show only if hard-surface rwy 3000ft↑
- airways: V(victor, black, VOR), T(tango, blue, GPS)
- reporting points: VHF fix [on VOR radial, triangle, required report when not in radar contact], GPS fix [without VOR possible, RNAV navigation waypoint, T-Routes, Q-routes]
- distance: plain number(leg), rounded(cumulative), square(total), COP(change over point)
- off airways navigation: VOR only & below 18000ft ? → max distance between NAVAIDs = 80NM
W/B
- forward: CG toward nose (stable)
- ↑stable(↓maneuverable), stall↑, TOL roll↑, cruise effi↓
- returns to level flight easily, harder to raise the nose, need↑elevator force
- aft: CG toward tail (maneuverable)
- ↑maneuverable(↓stable), stall↓, TOL roll↓, cruise effi↑fuel↑
- less stable, more likely to pitch up, less elevator force is needed